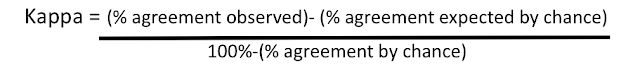Multiple testing refers to conducting more than one hypothesis test simultaneously
to make inferences on different aspects of a problem in a study experiment.
The significance level of a P value is defined under a single test.
When more than one test is conducted, simple use of the significance level for each
individual test leads to a probability of false-positive findings that is greater than
the stated α level.
Two commonly used approaches for choosing a significance level in multiple
testing are the FEW (“family-wise error rate”) and the FDR (False discovery rate).
False discovery rate
When a study involves a large number of tests, the FDR error measure is a more
useful approach in determining a significance cutoff because the FWE approach is
too stringent.
False discovery rate (FDR) is the expected proportion of the null hypotheses that
are falsely rejected divided by the total number of rejections.
Expected proportion of type 1 errors.
 PSM / COMMUNITY MEDICINE
PSM / COMMUNITY MEDICINE by
Dr Abhishek Jaiswal is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Based on a work at
learnpsm@blogspot.com.
Permissions beyond the scope of this license may be available at
jaiswal.fph@gmail.com.